13 – Configuring a Default Route (Gateway of Last Resort)#
This tutorial is the thirteenth in our Cisco Packet Tracer series and focuses on default routing—also known as configuring a gateway of last resort. This type of route is essential in smaller or stub networks, where routers only have one exit path for unknown destinations.
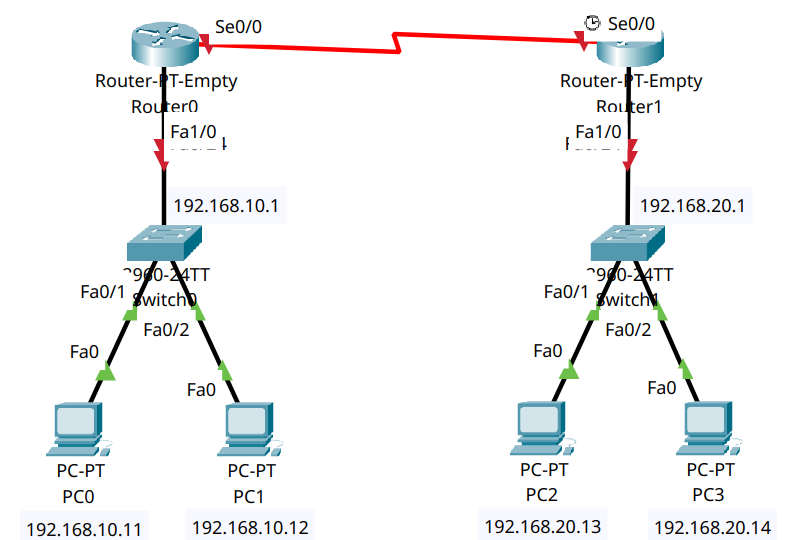
We will build a small branch-office style topology and configure the branch router to forward all unknown traffic to a main router using a static default route.
Find the CISCO pkt files in the repo -
Part 1 – Network Topology Overview#
This network includes:
Two routers (R0 = Branch, R1 = Main)
One switch per router (S0, S1)
Two PCs per switch (4 total PCs)
The branch site will have no knowledge of external networks, so it will use R1 as its gateway of last resort.
Part 2 – Device Placement and Cabling#
Step 2.1 – Add Devices to the Workspace#
From Network Devices and End Devices, place:
2 Routers (Router-PT-Empty)
2 Switches (2960)
4 PCs
Label the devices:
Routers: R0 (Branch), R1 (Main)
Switches: S0 (for R0), S1 (for R1)
PCs: PC0–PC3
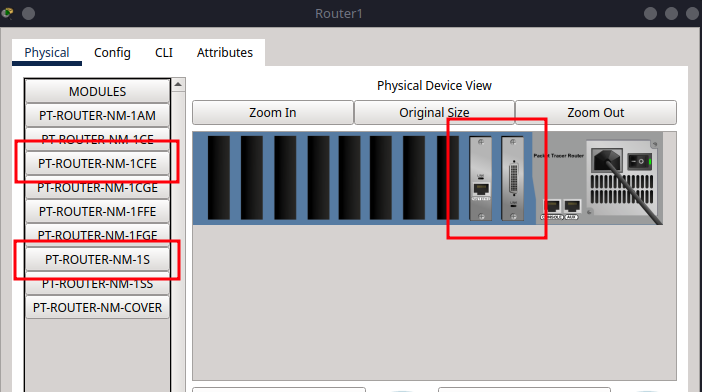
Step 2.2 – Add Network Modules to Routers#
Add:
1x PT-ROUTER-NM-1S
1x PT-ROUTER-NM-1CFE
Turn off each router, insert modules, then power back on.
If you need help with this, refer to the steps in How to Customise the Router-PT in Packet Tracer

Step 2.3 – Cabling#
Use Copper Straight-Through for PC to switch and switch to router connections. Use Serial DCE for the R0 ↔ R1 link.
From |
To |
Port/Interface |
|---|---|---|
PC0 |
S0 |
fa0/1 |
PC1 |
S0 |
fa0/2 |
S0 |
R0 |
fa0/24 → fa2/0 |
PC2 |
S1 |
fa0/1 |
PC3 |
S1 |
fa0/2 |
S1 |
R1 |
fa0/24 → fa2/0 |
R0 |
R1 |
se0/0 ↔ se0/0 |
Part 3 – IP Addressing Scheme#
Now we will assign IP addresses to all devices, ensuring they can communicate across the network.
Subnet Allocation#
For this tutorial, we will use the following subnets:
Subnet |
Devices |
Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|
192.168.10.0/24 |
PC0, PC1, R0 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.20.0/24 |
PC2, PC3, R1 |
255.255.255.0 |
10.0.0.0/30 |
R0 ↔ R1 |
255.0.0.0 |
Assign IPs to PCs#
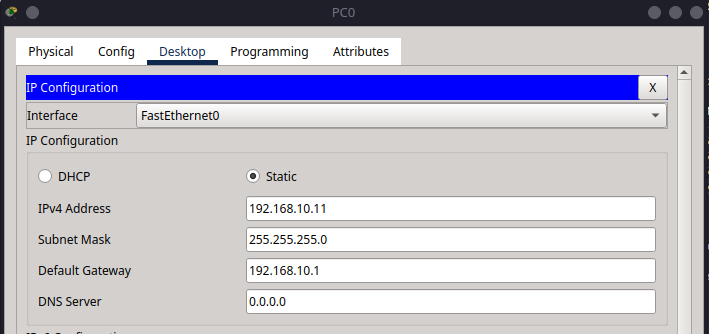
Go to Desktop > IP Configuration on each PC:
PC |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
PC0 |
192.168.10.11 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.10.1 |
PC1 |
192.168.10.12 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.10.1 |
PC2 |
192.168.20.13 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.20.1 |
PC3 |
192.168.20.14 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.20.1 |
Part 4 – Router Configuration#
In this part, we will configure the routers to enable communication between the PCs and set up a default route on R0.
Note
To ensure all unknown traffic from the branch site is forwarded to the main router, we configure a default route on R0. This is done with the command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2, which instructs R0 to send any traffic destined for networks it doesn’t know about to R1. On R1, we add a static route pointing back to the branch network, allowing two-way communication.
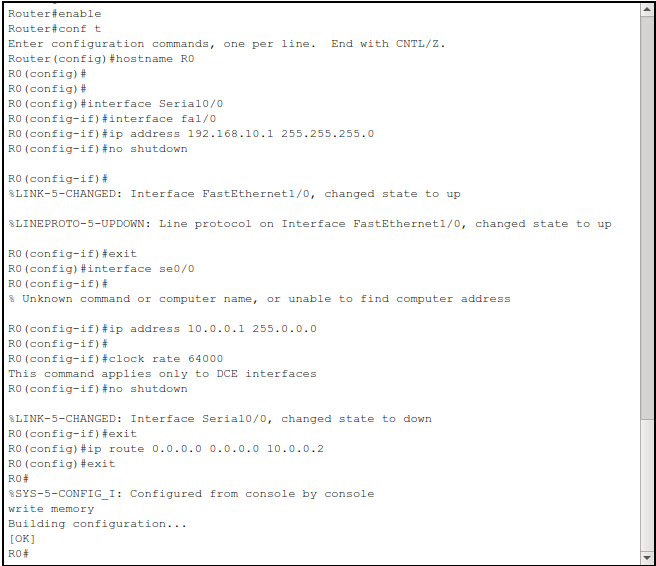
Step 4.1 – R0 (Branch Router)#
enable
configure terminal
hostname R0
interface fa1/0
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
interface se0/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
clock rate 64000
no shutdown
exit
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2
exit
write memory
This is the default route. It says: “Send all unknown traffic to
10.0.0.2(R1).”
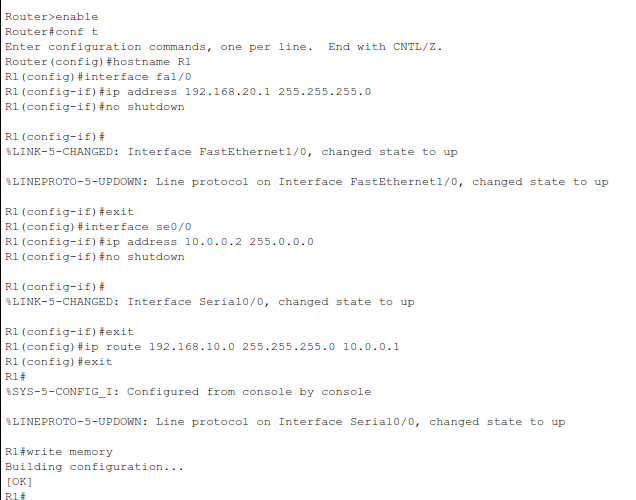
Step 4.2 – R1 (Main Router)#
enable
configure terminal
hostname R1
interface fa1/0
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
interface se0/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
no shutdown
exit
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1
exit
write memory
Part 5 – Verification and Testing#
Step 5.1 – Check Routing Tables#
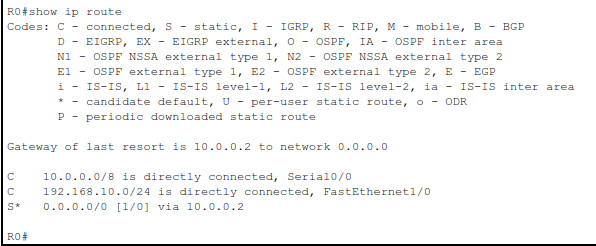
On R0:
show ip route
You should see a route labeled with S* – this is the static default route.
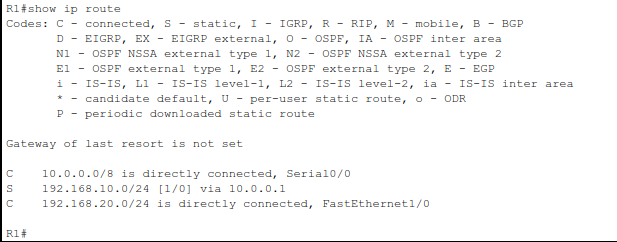
On R1:
show ip route
You should see a static route to 192.168.10.0 via 10.0.0.1
Step 5.2 – Ping Tests#
From PC0, try:
ping 192.168.20.10
ping 192.168.20.13
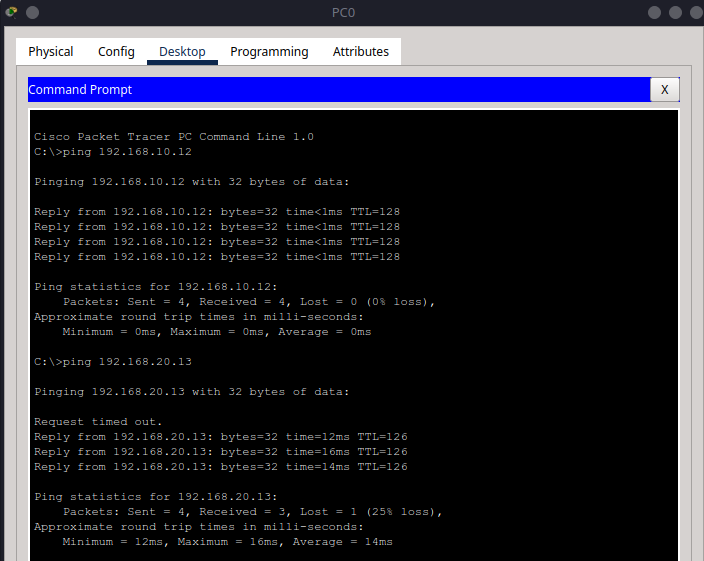
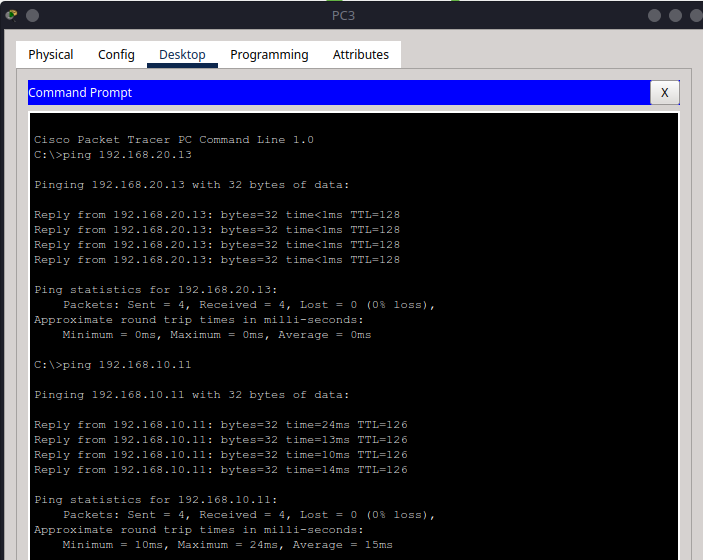
From PC3, try:
ping 192.168.20.13
ping 192.168.10.11
Summary#
In this tutorial, you:
Created a simple two-router topology
Assigned IP addresses and connected all devices
Configured a default route on the branch router
Verified full connectivity using
pingandshow ip route
Default routes are vital in small or remote networks where only one path leads to the rest of the network or the internet.